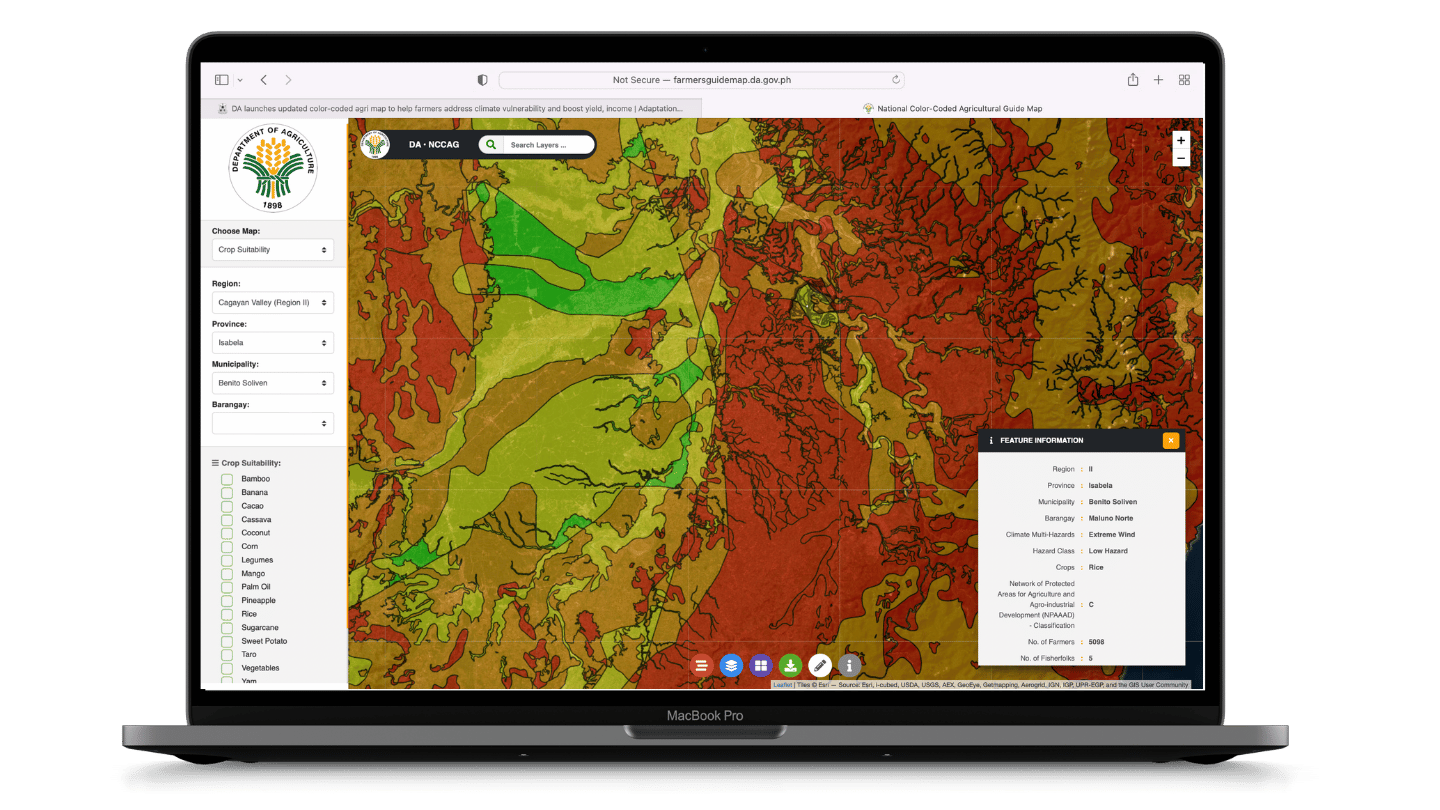
What is the National Color-Coded Agricultural Guide (NCCAG) Map?
The NCCAG Map is a database of map overlays that shows the natural suitability of economically-important crops that are key to food security. It identifies the crops that are most suitable in agricultural areas, and overlays data on soil properties, elevation, rainfall pattern, temperature and most importantly, the projected climate-induced multi-hazards. It features maps that are vital to crop growth and survivability such as water availability and climate data, as well as location-specific information on socio-economic conditions.
The first Decision-Support Tool developed under the DA AMIA Program, NCCAG supports the vision to remove the guesswork in Philippine agriculture by providing color-coded guide maps that identify the areas where crops could be ideally grown based on soil types, climatic conditions, and bio-physical requirements.
Where did the NCCAG Map source its data?
In coming up with the NCCAG Map, 29 thematic maps were obtained from different source agencies. Here are some of these agencies:




DA-Bureau of Soils and Water Management (for the soils map)
DENR - Mines and Geosciences Bureau (for geo hazards)
DOST PAGASA (for climate data)
DENR - Land Management Bureau (for land classification)



WorldClim (for climate data)
DENR - Natural Water Resources Board (for river basin and watershed boundaries, and groundwater potential)
UNFAO (for agro-ecological zones)




PSA (for political boundaries [not authoritative] and poverty data)
NEDA (for poverty data)
NAMRIA (for political boundaries [not authoritative])
DOST-PHIVOLCS (for rain-induced landslide and fault line data)
What are the features of the NCCAG Map?
Abaca, Bamboo, Banana, Cacao, Cassava, Coconut, Coffee, Corn, Legumes, Mango, Palm Oil, Papaya, Pineapple, Rice, Rubber, Sugarcane, Sweet Potato, Taro, Vegetables, Yam
Landslide, Erosion, Extreme, Wind, Drought, Sea Level Rise, Storm Surge, Salt Water Intrusion, and Flooding
A land resource mapping unit, defined in terms of climate, landform and soils, and/or land cover, and having a specific range of potentials and constraints for land use.
Choose from Baseline (1960 – 1990), 2020 – 2049 Forecast, and 2040 – 2069 Forecast.
Choose from Baseline (1960 – 1990), 2020 – 2049 Forecast, and 2040 – 2069 Forecast.
NAPAAAD is technically defined as prime agricultural lands where soils, topography and agro-climate are suitable for agriculture and fishery development.
Rice Suitability Zones based on data on existing rice areas from the Philippine Rice information SysteM (PRiSM)
Developed under the AMIA Program, the CRVA for crops provides information on exposure to climate-related risks and hazards, sensitivity of crops to changes in temperature and precipitation, and the adaptive capacity of communities to climate change. When combined, these would provide the overall vulnerability.
NCCAG provides information on the location of the AMIA Villages nationwide and their covered barangays.
What are the uses of the NCCAG Map?
The NCCAG Map aims to guide the government in determining forward-looking policies and site-specific food production projects and infrastructure investments.
As a decision support tool, it can be used for investment planning, climate-resilient research and development, innovative credit and insurance packages, climate-resilient agriculture and fisheries extension, infrastructure, and disaster management. It is useful for Local Government Units (LGUs) in preparing their local development plans, planning disaster risk reduction measures, and identifying suitable climate change adaptation technologies and practices.